Weird animal behaviors and odd antics could be signs of something bigger, like major environmental changes. It’s fascinating but also a little alarming to think about how these creatures might be responding to shifts in their habitats. So, let’s dive into some of these strange animal behaviors that might actually be red flags for environmental chaos.
1. Dolphins Beaching Themselves
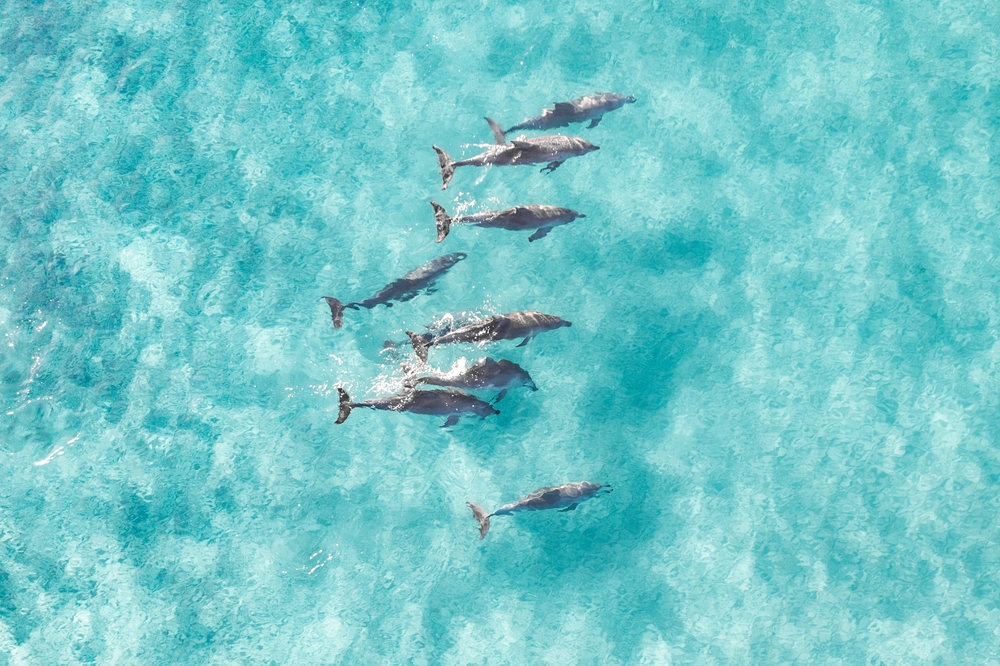
You may have heard about dolphins beaching themselves, and it’s as sad as it sounds. When dolphins, those intelligent, playful creatures of the sea, suddenly start washing ashore, it could be a big indicator of environmental imbalances. One study published in the “Journal of Marine Science” showed that increasing ocean temperatures and pollution are leading causes of this behavior. Dr. Emily Sorenson, a marine biologist, points out that when dolphins are stressed by these factors, their internal navigation systems can go haywire. So, next time you hear about beached dolphins, remember it’s not just a random tragedy but possibly a sign of something more problematic in our oceans.
In many cases, beaching is a desperate attempt by dolphins to escape polluted waters that have become inhospitable. They might be fleeing from harmful algal blooms or toxic substances that have infiltrated their habitats. You can imagine how stressful it must be for these social creatures to face an environment that’s literally poisoning them. By beaching themselves, they’re making a last resort attempt to survive, even though it’s usually a futile effort. This tragic behavior serves as a stark reminder that our oceans are under threat, and we need to pay attention.
2. Birds Flying Off Course
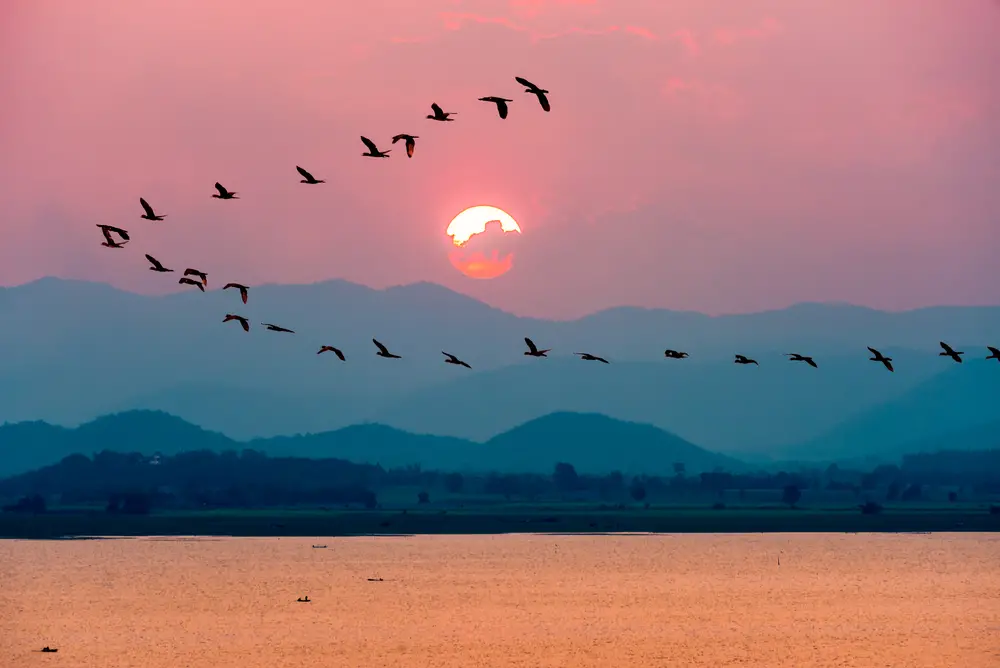

Ever noticed how sometimes flocks of birds seem to be flying in odd directions or ending up in places they shouldn’t? This could be another warning sign that something’s off in their environment. Changes in weather patterns, deforestation, and urbanization all play roles in disrupting migratory paths. Birds rely on natural cues like magnetic fields, stars, and landscapes to navigate, and when these are altered, birds can get completely disoriented. So, the next time you see a lost bird, it might be more than just a natural hiccup; it could be an environmental S.O.S.
Birds flying off course can also indicate a sudden shortage of resources in their regular routes. Maybe a once-thriving feeding ground is now barren due to drought or human activities. These disruptions force birds to wander further and become pioneers in unfamiliar territories. Unfortunately, this often leads to exhaustion and increased mortality rates as they struggle to find resources in new areas. These shifts highlight how interconnected our world is, and how the smallest changes can send ripples through the ecosystem.
3. Frogs Changing Colors
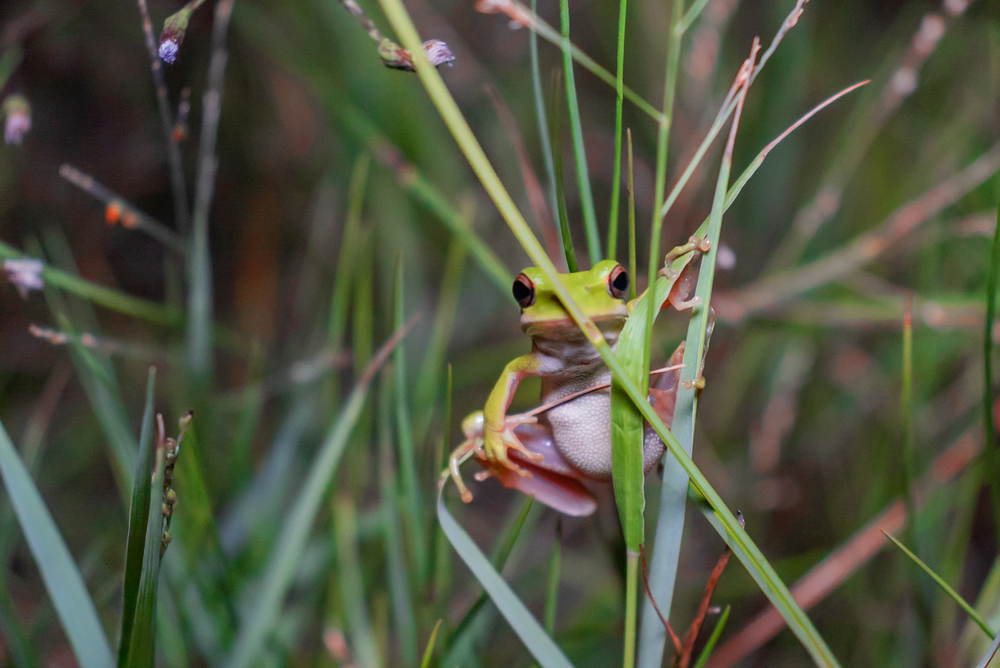

Have you seen frogs that seem to be swapping their usual colors for something more vibrant or unusual? Frogs changing colors is not just a neat trick; it’s often a response to environmental stress. A study from the University of Queensland suggests that pollution and climate change are affecting frogs’ skin colors as a defensive mechanism. Dr. Jenna Kerr, an expert in amphibian biology, explains that these color changes can be a reaction to increased UV radiation or pollutants in their habitats. It’s a survival tactic, but it’s also a red flag that their environment is struggling.
When frogs change colors, it can indicate that their skin is attempting to adapt to new, harsher conditions. These adaptations are not always successful and can lead to increased vulnerability to predators or other environmental hazards. The more frequent and drastic these color changes become, the more they point to significant shifts in their ecosystems. For frogs, whose delicate skin is so sensitive to environmental changes, this behavior signals alarms we shouldn’t ignore. It’s a vivid reminder of how sensitive and responsive animals are to their changing world.
4. Polar Bears Approaching Human Habitats
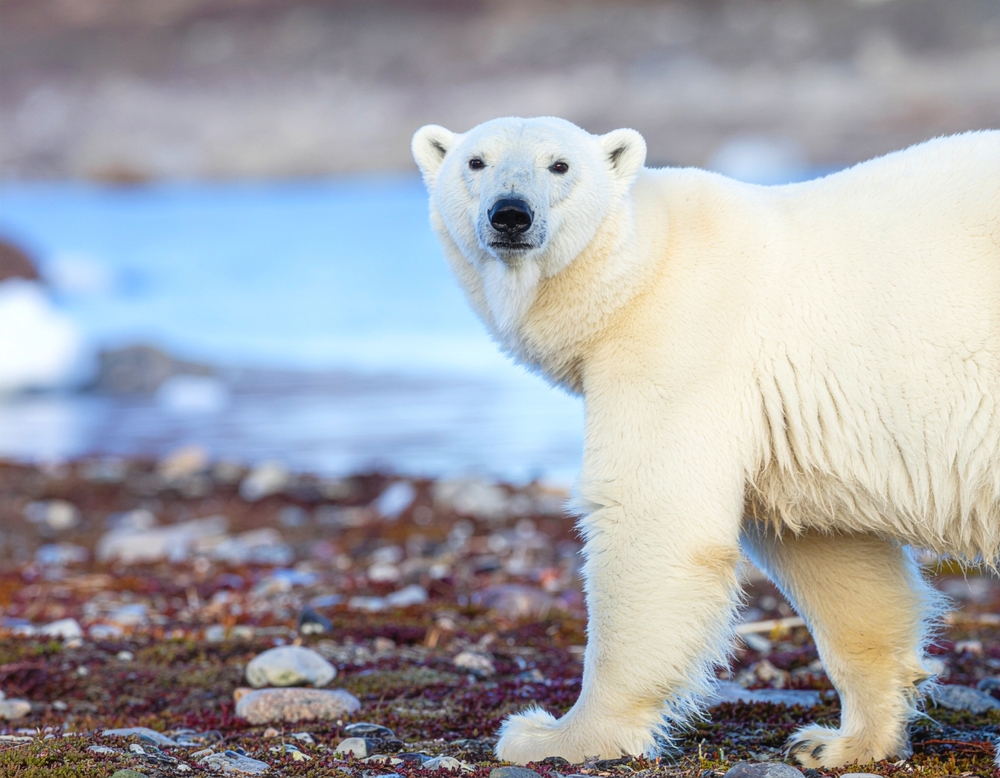

Imagine seeing a polar bear, a creature normally isolated in icy wilderness, wandering into towns looking for food. This isn’t just an adventurous bear taking a wrong turn—it’s a sign of shrinking ice caps and dwindling food supplies. As climate change reduces their natural hunting grounds, polar bears are forced to venture further to find sustenance. This journey often leads them into human territories, creating dangerous situations for both bears and people. So, when polar bears start showing up uninvited, it’s a clear signal that their world is melting away.
These majestic creatures are finding it increasingly difficult to catch seals, their primary food source, as sea ice continues to vanish. With less ice to hunt on, polar bears spend more time and energy searching for food, increasing fatigue and lowering reproductive rates over time. As a result, they’re moving closer to human settlements, scavenging for alternatives like garbage or pet food. This behavior isn’t just a nuisance; it’s an urgent cry for help from a species on the brink. Seeing polar bears in cities is a dramatic and heart-wrenching reminder of how climate change affects wildlife.
5. Fireflies Disappearing
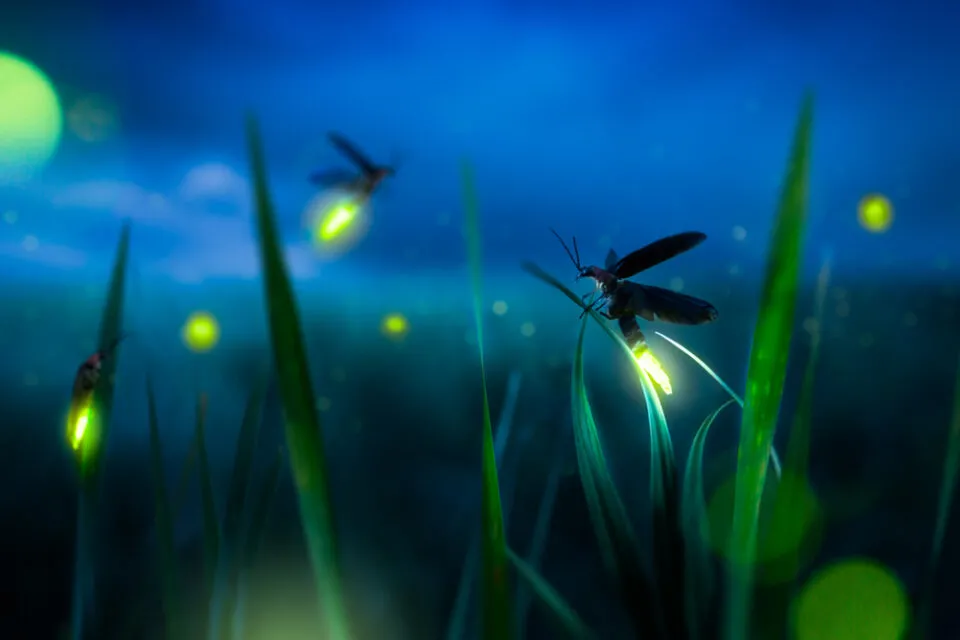

Remember catching fireflies as a kid, those tiny sparks lighting up the summer nights? If you’ve noticed fewer fireflies around, it’s not just nostalgia playing tricks on you. Research from Tufts University highlights that habitat destruction and light pollution are major culprits in the decline of firefly populations. Dr. Sara Lewis, who led the study, notes how these factors disrupt the fireflies’ mating rituals, which rely heavily on their bioluminescent signals. So, the vanishing glow of fireflies is more than just a loss of childhood magic; it’s a serious environmental issue.
Fireflies rely on specific conditions to thrive, including moisture-rich areas and dark, unpolluted night skies. As urbanization spreads and wetlands are drained, fireflies lose their habitats, forcing them to relocate or perish. Moreover, excessive artificial lighting can confuse or drown out the natural signals fireflies use to find mates. This not only threatens their reproduction but also signals wider issues of ecological imbalance. If these glowing beetles continue to disappear, it’s a clear indication that we’re losing ground in maintaining the natural balance of our habitats.
6. Bees Going Missing
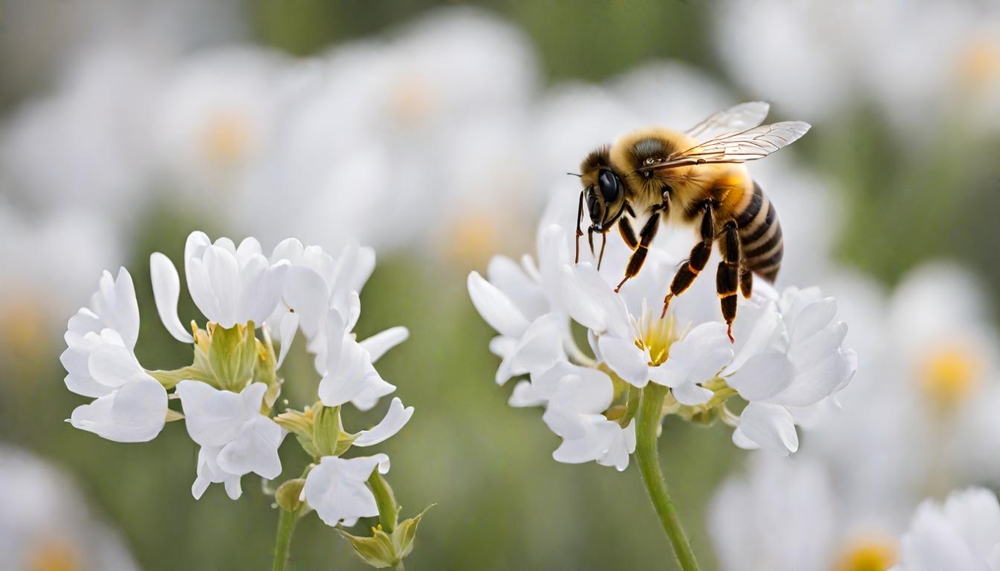

We’ve all heard the buzz about bees disappearing, but what’s really going on? The phenomenon known as Colony Collapse Disorder has been a mystery and concern for environmentalists and farmers alike. Bees are crucial pollinators, and their decline can lead to significant drops in crop yields, affecting global food supply. Factors like pesticides, disease, and habitat loss are contributing to this alarming trend. When bees start vanishing, it’s not just a loss of honey; it’s a signal that our agricultural systems could be on the brink of chaos.
Bees have a complex social structure that relies on a delicate balance within their environment. When this balance is disrupted, the entire colony can fail, leaving hives empty and silent. This not only affects the bees but also the plants they pollinate, leading to broader ecological consequences. The decline in bee populations underscores the importance of sustainable farming practices and the urgent need for policy changes. The missing bees are a small symptom of a much larger problem that demands our attention.
7. Fish Swimming Towards Warm Waters
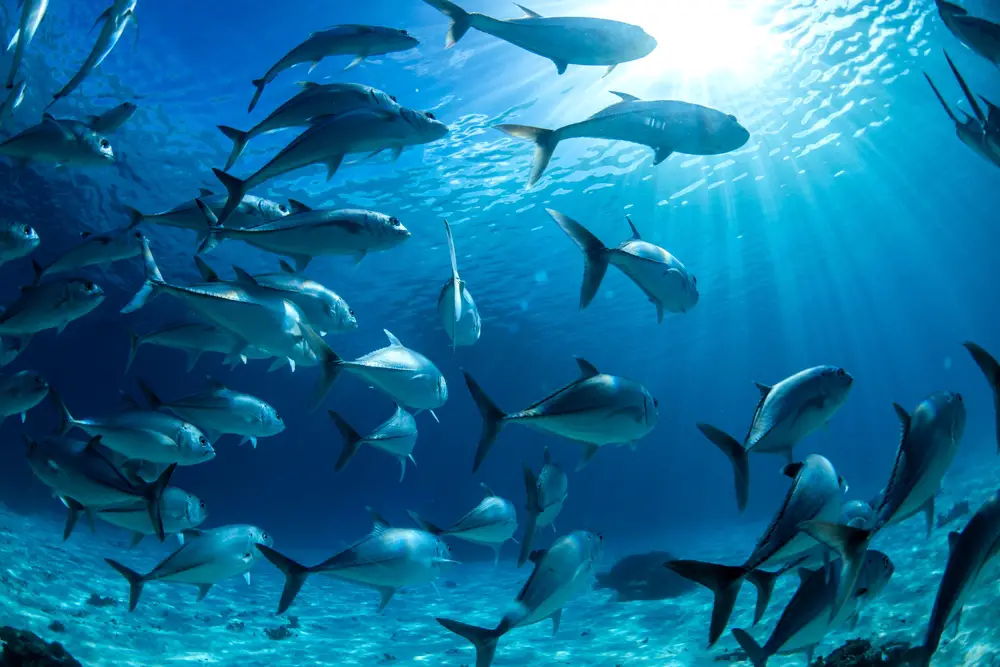

If you’re into fishing or just enjoy marine life, you might have noticed certain fish species appearing in places they never used to inhabit. Fish swimming towards warmer waters is a growing trend influenced by climate change and rising sea temperatures. A report from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) notes that many species are migrating northward or into deeper, cooler areas. Dr. Richard Jones, a marine ecologist, emphasizes how this shift disrupts local ecosystems and fishing industries as fish abandon their traditional habitats. So, when fish start moving to new digs, it’s a clear sign that the ocean’s climate is shifting.
This migration can lead to overpopulation in some areas and scarcity in others, creating a ripple effect throughout the food chain. Predator-prey relationships are altered, causing some species to thrive while others decline. As fish relocate, fishermen face changing opportunities and challenges, impacting livelihoods and economies. These shifts in fish populations reflect broader changes in oceanic conditions that are hard to ignore. It’s a reminder that climate change is not just a distant threat but a current reality affecting life beneath the waves.
8. Butterflies Emerging Early
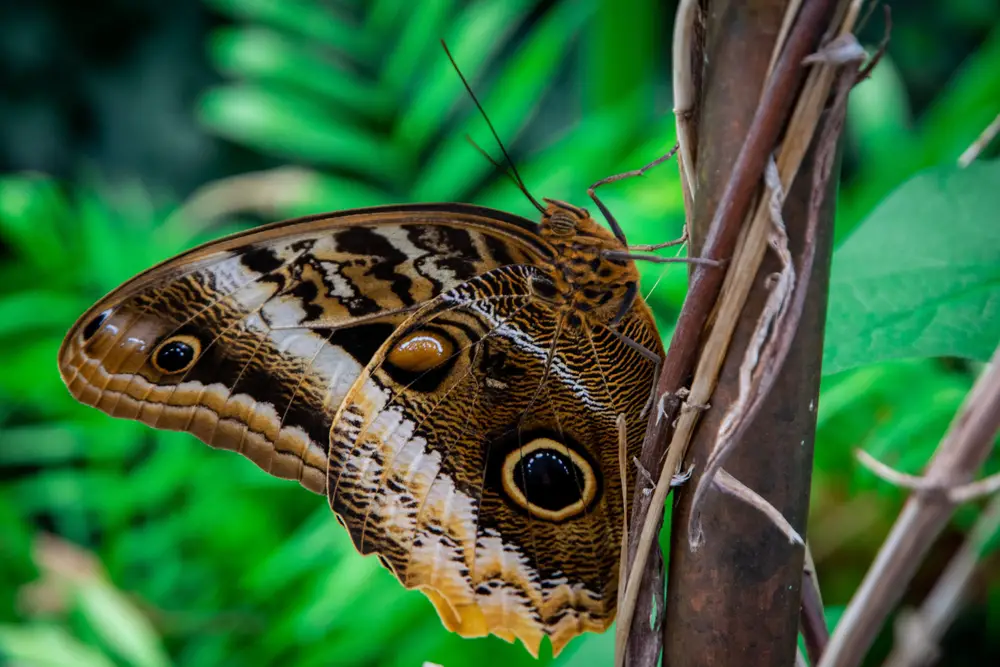

Have you noticed butterflies fluttering about earlier than usual in the year? This isn’t just a nice surprise but rather an indicator of shifting seasons. As global temperatures rise, many butterfly species are emerging weeks earlier than their historical patterns. This change can throw off the timing of their life cycles, affecting their survival and reproduction rates. So, when butterflies start appearing too soon, it’s a colorful but concerning sign of climate change’s impact on natural timing.
The early emergence of butterflies can lead to mismatches between their life cycles and the availability of food sources. Flowers may not be in bloom yet, leaving these early arrivers without nectar to sustain them. This can lead to decreased populations as butterflies fail to reproduce successfully. It also impacts plants that rely on butterflies for pollination, disrupting an essential ecological process. This shift in butterfly behavior is a small, visible manifestation of the broader effects of climate change on our ecosystems.
9. Whales Stranding Themselves
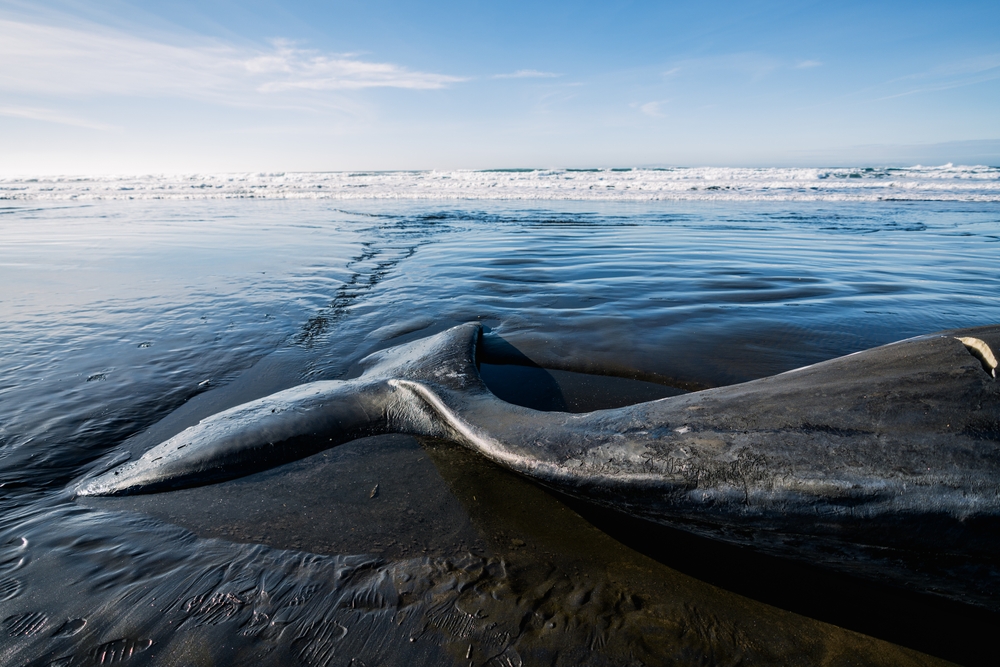

Whales are among the ocean’s most majestic creatures, so seeing them stranded on shores is particularly distressing. While whale strandings aren’t entirely new, their increasing frequency is a worrying sign. Factors like sonar disruption, pollution, and shifting prey availability due to climate change are all contributing causes. When whales beach themselves, it’s not just a tragic accident; it’s often a signal that something is seriously wrong in their underwater world. Each stranding serves as a reminder of the fragility of marine ecosystems.
The causes of whale stranding are complex and often involve multiple environmental stresses. Sonar and underwater noise pollution can interfere with whales’ navigation systems, leading them off course. Meanwhile, changes in water temperature and prey distribution can force whales into unfamiliar waters. Unfortunately, once whales are stranded, they face a slim chance of survival. These events highlight the urgent need for greater protection and conservation efforts for marine life.
10. Turtles Nesting Out Of Season
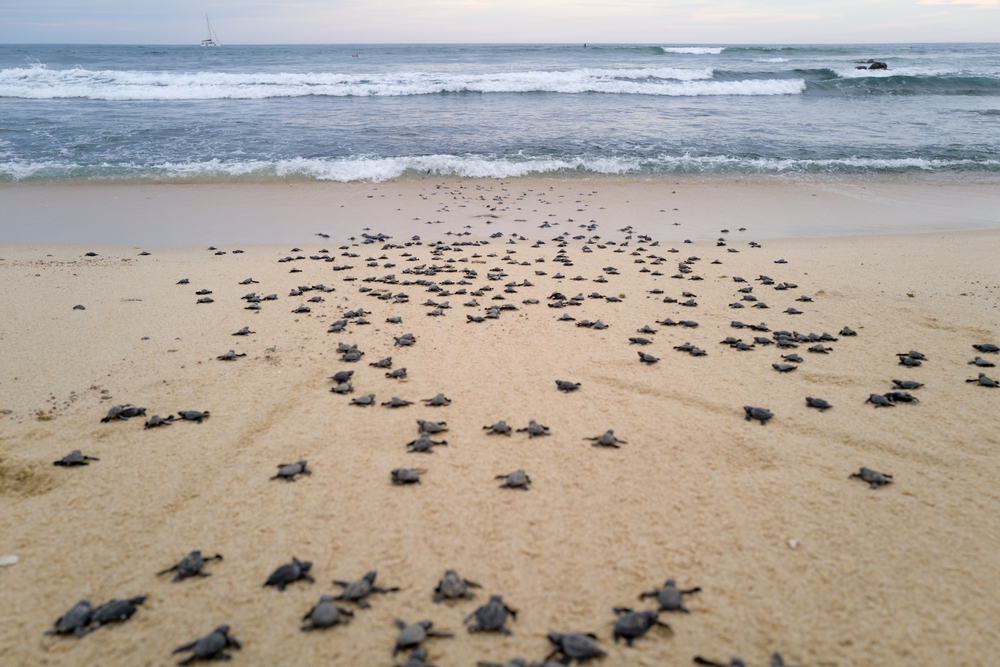

Have you come across news of turtles nesting out of season? This unusual behavior is becoming more common and is closely linked to climate change. As global temperatures rise, the nesting patterns of sea turtles are being disrupted, causing them to lay eggs at atypical times. This can lead to lower hatchling survival rates as the conditions may not be ideal for egg incubation. When turtles start nesting off-schedule, it’s a sign that their natural rhythms are being thrown off by environmental changes.
Turtles rely on specific environmental cues to signal the right time for nesting. When these signals are altered, turtles may lay eggs too early or too late, affecting the development of young turtles. Early hatchlings might face predation or lack of food, while late ones might not survive the colder temperatures. These disruptions can have long-term effects on turtle populations, which are already vulnerable. Turtles nesting out of season is more than just a peculiarity; it’s a significant concern for their conservation.
11. Wolves Hunting In Packs More Frequently
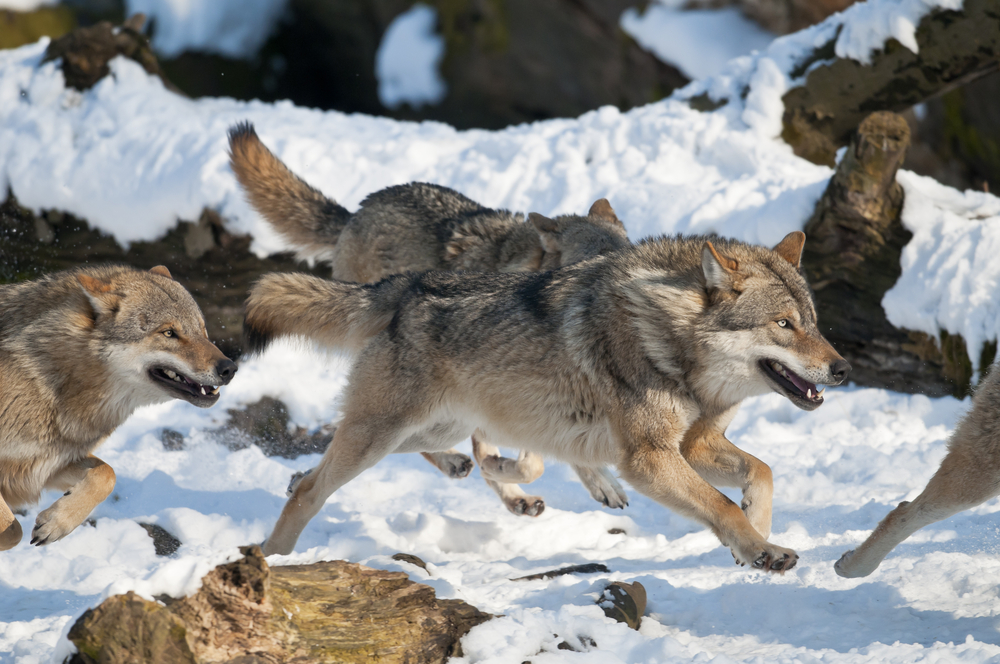

You might think wolves always hunt in packs, but increased pack hunting can signal something unusual. Wolves usually adapt their hunting strategies based on prey availability and environmental conditions. As their traditional prey becomes scarce due to habitat loss and climate shifts, wolves may band together more frequently to improve hunting success. This behavior suggests that wolves are struggling to find enough food. When you see wolves hunting in larger groups, it could be a clue that their ecosystem is under stress.
Pack hunting is an efficient strategy, but it also requires more energy and cooperation among wolves. When resources are scarce, larger packs can put additional pressure on available prey, leading to further ecological imbalance. It’s a survival tactic born out of necessity, reflecting the broader challenges faced by predators in a changing world. Observing these changes in wolf behavior offers insights into the health of their habitats. It’s a powerful reminder of how interconnected predator and prey dynamics are with the environment.
12. Elephants Changing Migration Patterns
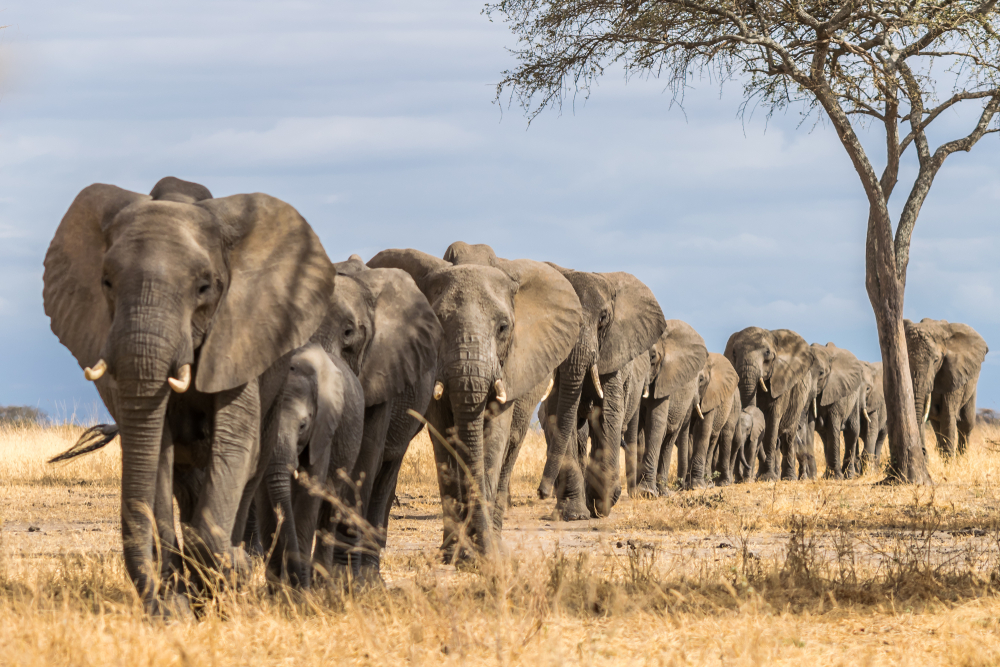

Have you ever wondered why elephants might change their migration paths? When elephants start taking unfamiliar routes, it often means their natural habitats are changing, sometimes drastically. Deforestation, agricultural expansion, and climate change are key factors disrupting their traditional migratory patterns. This behavior indicates that elephants are searching for new sources of food and water as their usual resources become scarce. It’s a poignant sign that these gentle giants are struggling to adapt to their rapidly changing world.
The alteration of migration patterns can have significant impacts on elephant populations and the ecosystems they interact with. Elephants play a crucial role in shaping their environment, and changes in their movements can affect biodiversity and habitat structure. When elephants are forced to travel through human-populated areas, it can also lead to increased human-wildlife conflicts. These shifts highlight the need for conservation efforts that protect elephant habitats and promote coexistence. Watching elephants wander into new territories is a sign that their traditional landscapes are under threat.
13. Rodents Acting Aggressively
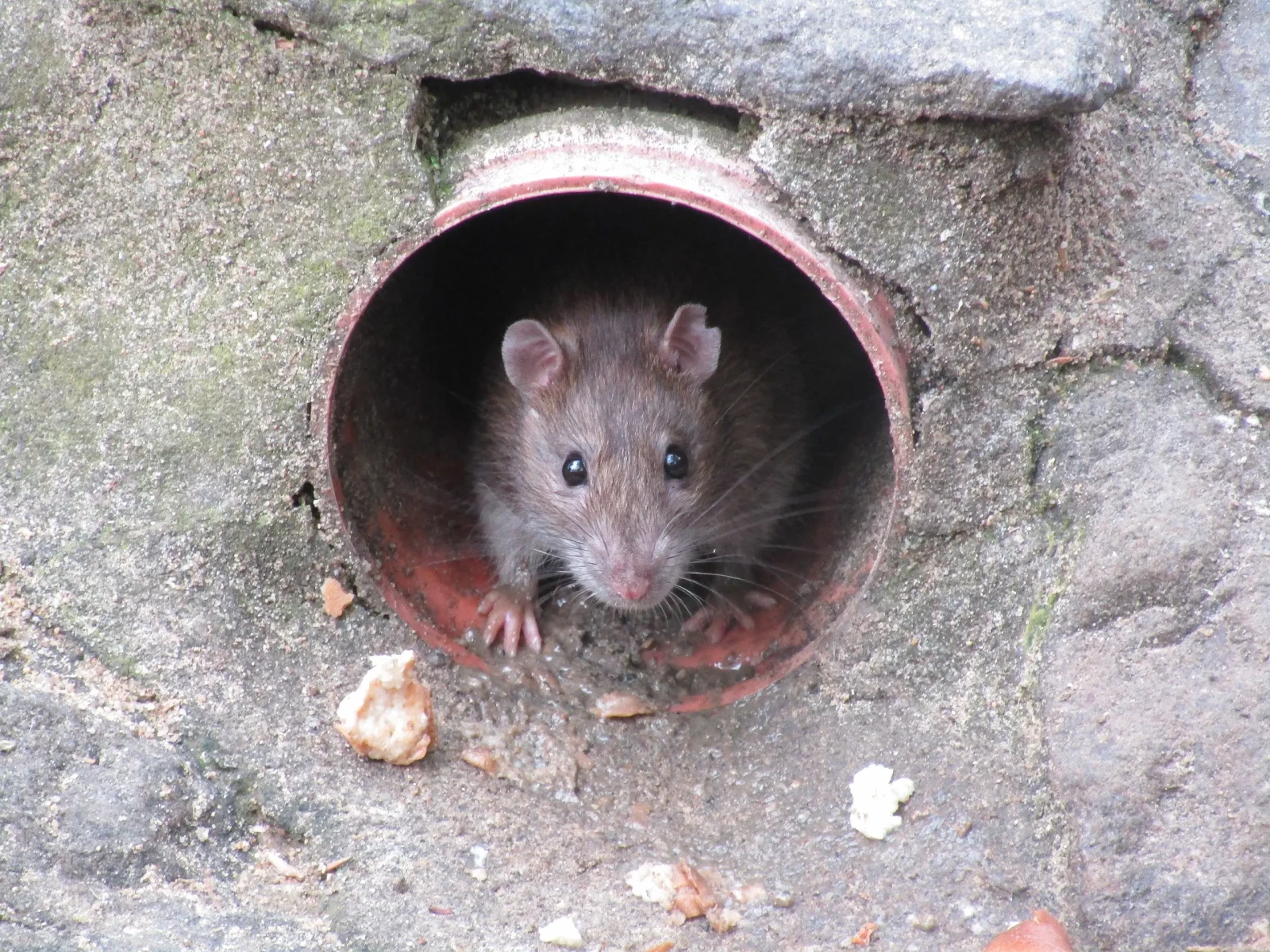

Have you ever noticed rodents behaving more aggressively than usual? This change in behavior could be a response to environmental pressures such as overcrowding, lack of food, or habitat shifts. As humans encroach on natural areas, rodents often find themselves competing for limited resources. Increased aggression is a survival tactic, but it’s also a symptom of a stressed ecosystem. When rodents start acting out, it’s a sign that their world, and possibly ours, is out of balance.
Rodent aggression can lead to a higher spread of diseases and increased competition among species. It’s a behavior that reflects broader ecological tensions, often triggered by rapid changes in environmental conditions. These changes can include urban development, climate-induced food scarcity, and changes in predator populations. As a result, rodents may invade human habitats with greater frequency, seeking food and shelter. The aggressive behavior of rodents is a warning that ecosystems are being pushed to their limits.
