In today’s world, pollution is an unfortunate reality impacting ecosystems across the globe. However, in the face of adversity, some animals have developed incredible adaptations, allowing them to thrive in even the most toxic environments. Let’s take a closer look at ten remarkable creatures that have managed to survive—and even flourish—in the places where pollution is at its worst. As we explore these resilient animals, consider how their unique adaptations paint a picture of nature’s incredible resilience.
1. The Indestructible Cockroach: Nature’s Unlikely Survivor
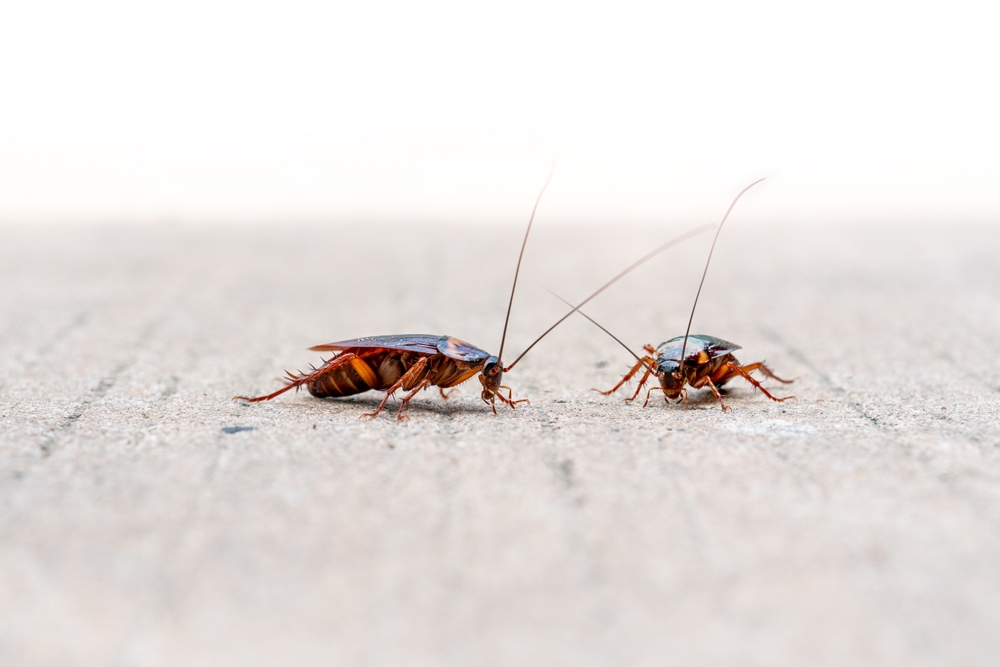

We’re kicking off our list with an animal that’s become synonymous with resilience: the cockroach. Cockroaches have been around for millions of years, and their ability to adapt to harsh environments is legendary. In urban areas with high pollution levels, these little critters have not only survived but thrived. Their bodies can tolerate a wide range of toxic substances, allowing them to make a meal out of materials that would be deadly to other organisms. According to National Geographic, certain species can even hold their breath for up to 40 minutes, avoiding inhaling harmful substances.
Furthermore, cockroaches have developed a remarkable resistance to pesticides, which makes controlling their populations a challenge in polluted cities. They reproduce quickly and can live off minimal resources, often scavenging in areas with heavy industrial waste. This adaptability and resilience make them a permanent fixture in environments that would otherwise be inhospitable. Love them or hate them, you have to admire their tenacity in the face of pollution.
2. Pigeons: The Urban Warriors
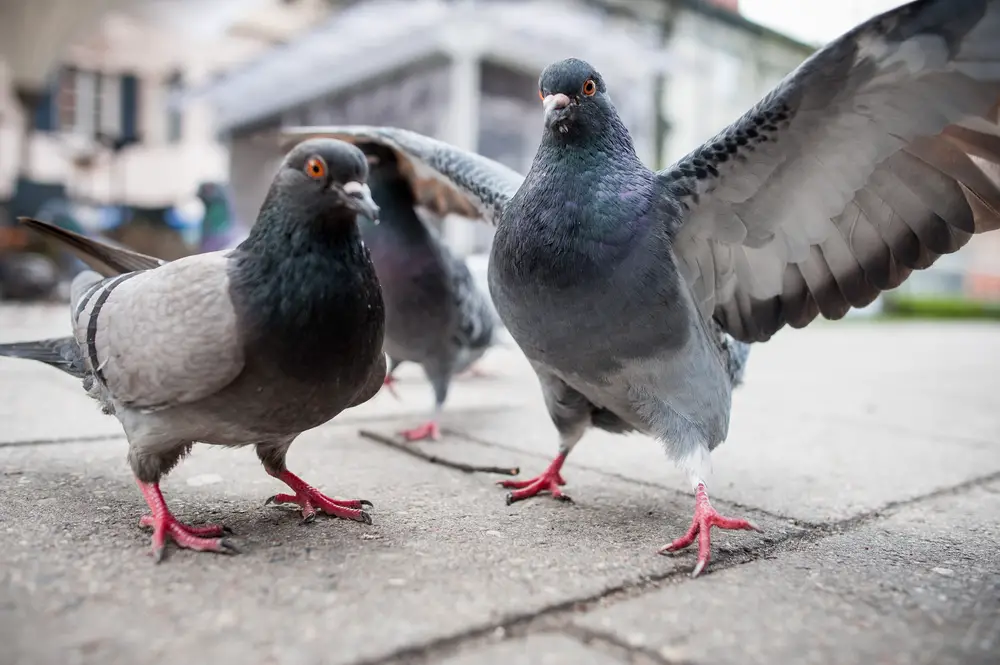

Pigeons might be the most common city bird around the world, and they’ve certainly earned their reputation as resilient urban dwellers. In cities plagued by air pollution and garbage, these birds have learned to adapt remarkably well. Their diet is incredibly flexible, allowing them to consume a variety of foods, including those that might be laced with toxins. This adaptability helps them survive in environments that are often unkind to more selective eaters. According to the BBC, pigeons have also developed a knack for navigating through smog-filled skies, using their acute sense of direction.
In addition to their dietary flexibility, pigeons have evolved to thrive in the urban jungle’s harsh climate. Their feathers often trap pollutants, which might seem hazardous, but these birds have shown a remarkable ability to detoxify and cope with the stress of urban living. Despite their reputation as pests, pigeons play a vital role in the urban ecosystem as seed dispersers and food sources for urban predators. Their success in polluted environments showcases their impressive adaptability and the broader resilience of avian species.
3. Rats: The Ultimate City Dwellers
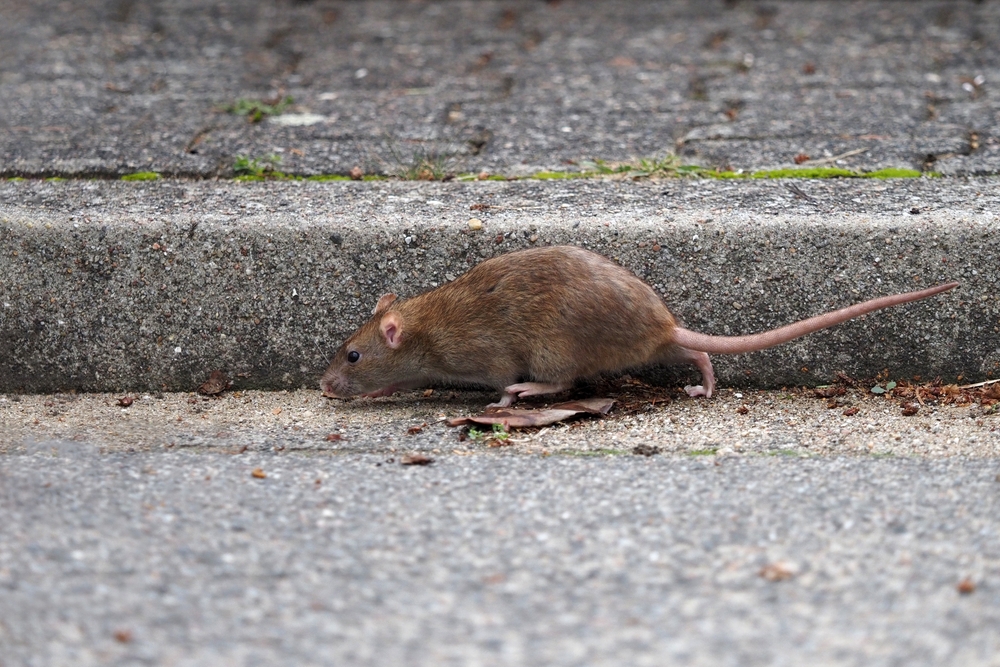

Rats are often found in the world’s most polluted cities, and they’ve become masters of urban survival. These intelligent rodents have adapted to thrive amidst human-created chaos, scavenging what they can from our waste. Their omnivorous diet allows them to consume a wide variety of foods, and their keen sense of smell helps them locate meals even in the dirtiest of environments. Scientists have discovered that urban rats have developed a unique resilience to certain toxins, which helps them survive in areas with high pollution levels. Learn more about how rats have adapted to city life from National Geographic.
Rats are not just scavengers; they’re also highly social creatures, which aids in their survival. They communicate and coordinate with one another to find resources and avoid danger, making them even more adept at navigating polluted environments. Their adaptability is further evidenced by their ability to build complex burrow systems in urban areas, providing shelter and a base for their community. While they might not be the most beloved creatures, rats have shown remarkable ingenuity and resilience in the face of pollution.
4. Crows: The Crafty Clean-Up Crew
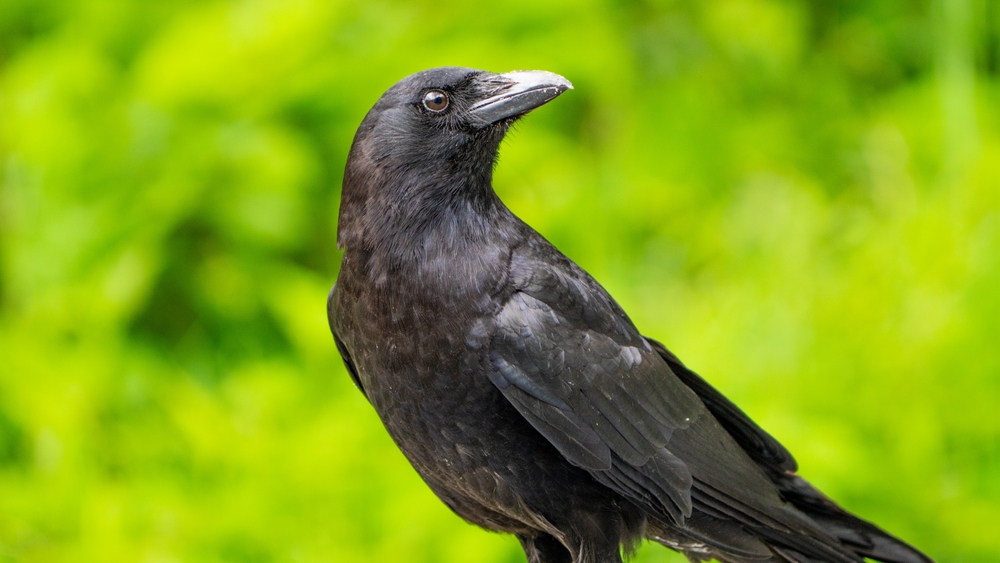

Crows are often seen as nature’s cleanup crew, and for a good reason. These highly intelligent birds have learned to thrive in polluted environments, especially in cities where waste is abundant. Crows possess an impressive ability to solve complex problems, allowing them to access food sources that might be out of reach for other animals. Their adaptability extends to their diet, as they’re capable of consuming a wide array of foods, including leftovers and even small animals that survive in polluted areas.
In addition to their dietary flexibility, crows have a knack for using tools, which is a testament to their intelligence. They’ve been observed dropping nuts onto roads for cars to crack open or using sticks to extract food from crevices. This innovative behavior allows them to thrive in environments where other birds might struggle. Crows also play a crucial role in the ecosystem by helping to control pest populations, providing a natural service that benefits both humans and the environment.
5. Tilapia: Swimming in Polluted Waters
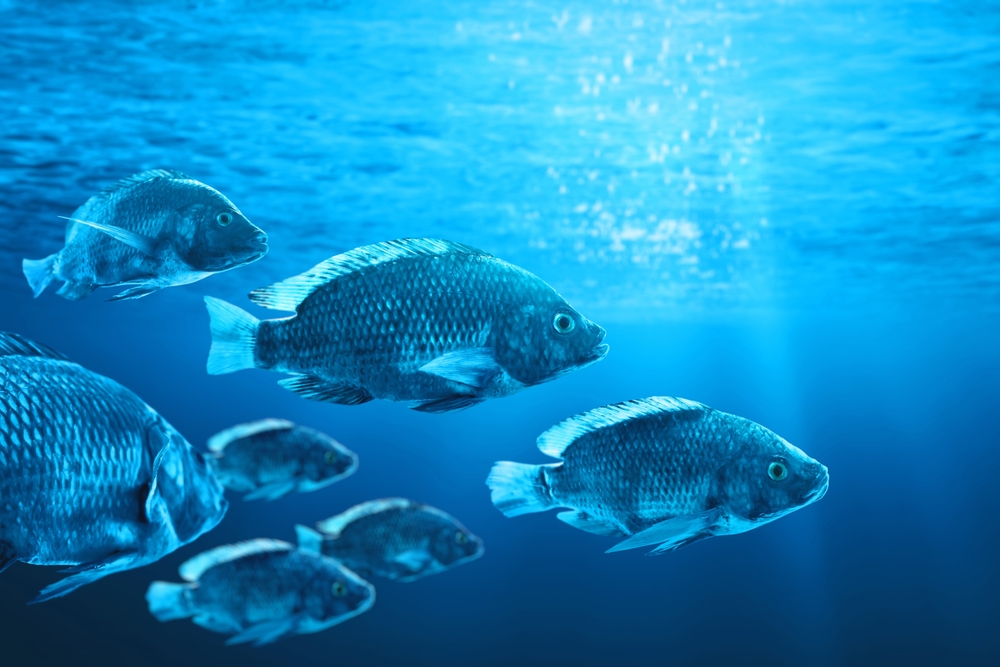

Tilapia, a hardy freshwater fish, is a staple in aquaculture around the world. Surprisingly, they have also adapted to survive in polluted waters, often found in rivers and lakes with high levels of industrial waste. Their ability to tolerate low oxygen levels and high concentrations of pollutants makes them uniquely suited to these challenging environments. This resilience is partly due to their efficient respiratory systems and an ability to filter feed on algae and other aquatic vegetation, which thrive in nutrient-rich, polluted waters.
Their adaptability doesn’t end with their diet. Tilapia can reproduce quickly, which allows their populations to recover from environmental stresses more rapidly than other species. Despite their ability to thrive in less-than-ideal conditions, the health of their habitats is crucial for their long-term survival. Efforts to clean polluted waters not only benefit tilapia but also the entire aquatic ecosystem. These fish serve as a reminder of nature’s resiliency and the importance of maintaining healthy environments for all species.
6. Mosquitoes: Masters of Adaptation
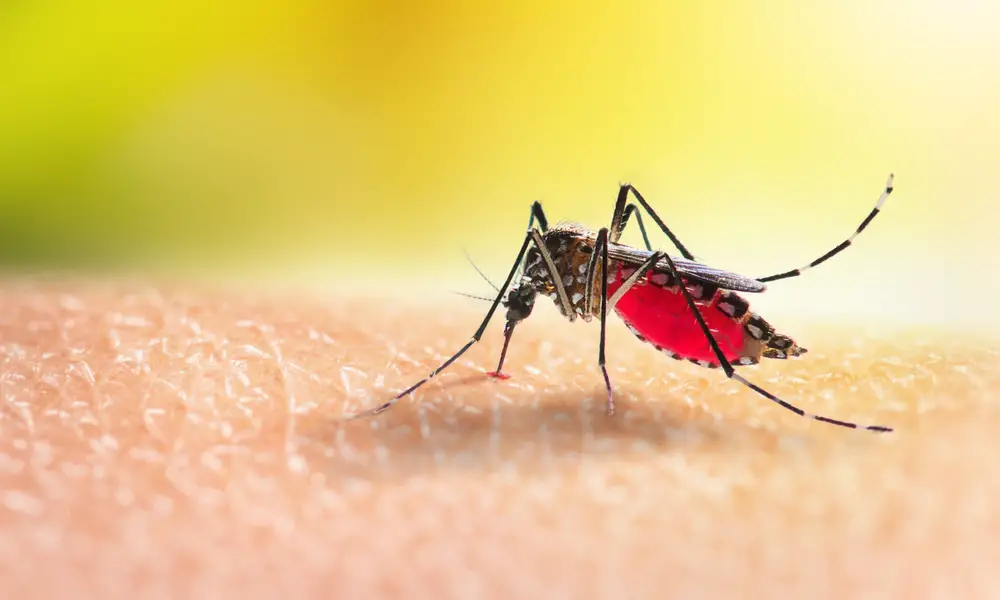
The ubiquitous mosquito is a testament to nature’s adaptability, thriving in polluted environments worldwide. These tiny insects have developed a remarkable tolerance for various pollutants, allowing them to lay their eggs in stagnant, contaminated water sources. Mosquito larvae possess specialized adaptations that enable them to survive in environments lacking oxygen and teeming with toxins. This resilience is further enhanced by their rapid reproductive cycle, which allows them to quickly repopulate even in harsh conditions.
Despite their small size, mosquitoes play a complex role in the ecosystem. They are a food source for many animals, including birds and bats, and play a role in pollination. However, they are also vectors for diseases, making their presence in polluted areas a public health concern. While their adaptability is admirable, it also highlights the need for effective management strategies to control their populations and mitigate the risks they pose to human health. Mosquitoes are a powerful reminder of both nature’s resilience and the challenges posed by pollution.
7. Seagulls: The Opportunistic Feeders

Seagulls have long been associated with coastal environments, but they’ve also adapted to thrive in polluted areas, especially around urban centers. These birds are incredibly opportunistic feeders, capable of subsisting on a diet of human waste, discarded food, and small animals found in polluted waters. Their strong digestive systems allow them to process a wide variety of foods, including those contaminated with toxins. This flexibility is a key factor in their ability to survive and prosper in areas where pollution levels are high.
In addition to their dietary adaptability, seagulls have become adept at navigating urban landscapes. They’ve been known to nest on rooftops, scavenge in landfills, and even frequent parking lots in search of food. This ability to exploit human-altered environments has helped them maintain stable populations despite the challenges posed by pollution. Seagulls provide a fascinating example of how animals can adjust to changing conditions and find new ways to survive in the face of adversity.
8. Raccoons: The Nighttime Foragers
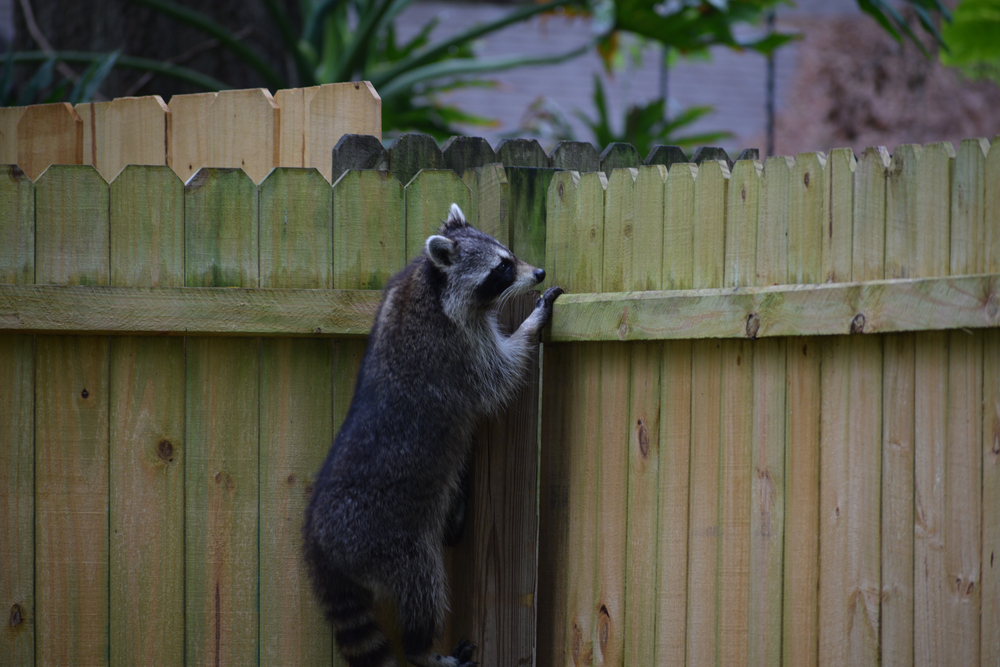

Raccoons are known for their cleverness and adaptability, allowing them to thrive in various environments, including polluted urban areas. These nocturnal foragers have a highly varied diet, which includes everything from fruits and nuts to small animals and human garbage. Their dexterous front paws are adept at manipulating objects, enabling them to access food sources that might be inaccessible to other animals. This skill, coupled with their ability to learn and remember, makes them formidable survivors in polluted settings.
Raccoons have also adapted to urban landscapes by finding shelter in man-made structures, such as attics and abandoned buildings. Their resourcefulness is evident in their ability to navigate complex environments and exploit available resources. While their presence in cities can sometimes lead to conflicts with humans, raccoons play an essential role in the urban ecosystem by helping to control pest populations. Their adaptability is a testament to the resilience of wildlife in the face of pollution and urbanization.
9. Catfish: Bottom Dwellers in Contaminated Waters
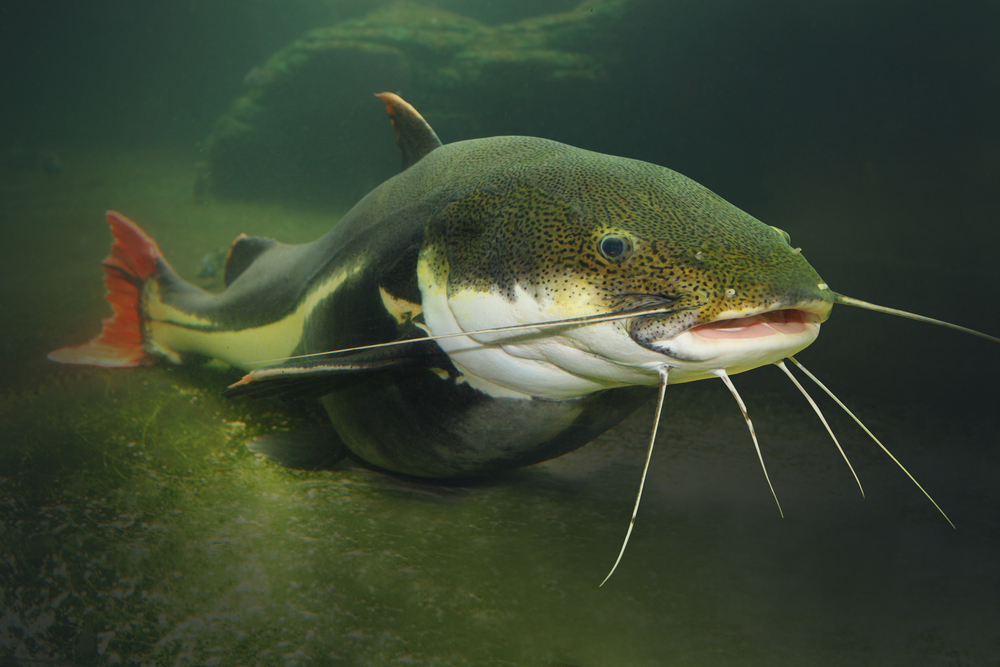

Catfish are renowned for their ability to survive in some of the most contaminated waters on the planet. These bottom-dwelling fish have adapted to environments with low oxygen levels and high pollutant concentrations. Their barbels, or “whiskers,” are equipped with taste buds that help them locate food in murky waters where visibility is low. This sensory adaptation allows them to thrive in polluted rivers and lakes where other fish might struggle to survive.
In addition to their impressive sensory abilities, catfish possess a robust immune system that helps them withstand the adverse effects of pollution. This resilience has enabled them to maintain stable populations even in heavily contaminated habitats. Their presence serves as an indicator of the health of aquatic ecosystems and highlights the importance of addressing pollution to protect biodiversity. Catfish remind us of the intricate connections within ecosystems and the need to preserve and restore natural habitats.
10. Peregrine Falcons: The Sky’s Resilient Predators
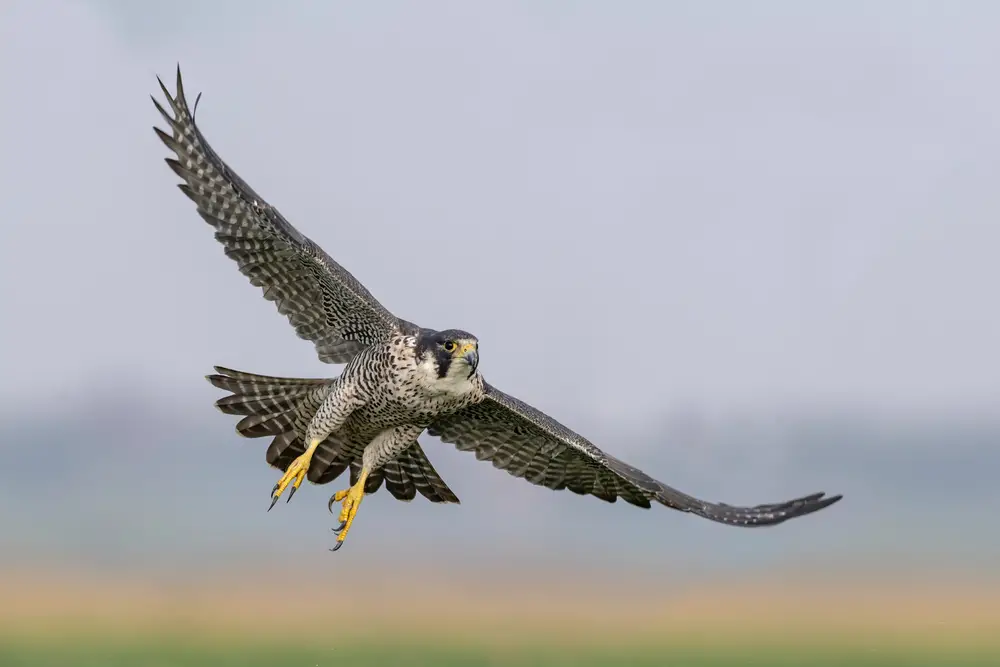

Peregrine falcons are among the most revered avian predators, and they’ve made remarkable comebacks in urban environments. These birds have adapted to living on skyscrapers and tall structures, which mimic the cliffs they naturally prefer. Urban areas, despite their pollution, offer abundant food sources in the form of pigeons and other small birds. Peregrine falcons are opportunistic hunters, and their incredible speed and agility allow them to capture prey even in challenging urban settings.
Their ability to thrive in polluted areas is a testament to their adaptability and resilience. Conservation efforts have played a significant role in their recovery, demonstrating the potential for positive change in urban ecosystems. Peregrine falcons serve as a symbol of hope, showcasing how wildlife can persevere and flourish even in the face of pollution and human impact. These remarkable birds remind us of the importance of protecting and supporting the biodiversity that exists within our cities.
